AI-Ready Assessment Integrity: A Practical Framework for 2026
Academic integrity is shifting quickly as AI becomes part of everyday study. In the HEPI Student Generative AI Survey 2025, 92 percent of students reported using AI, up from 66 percent in 2024, and 88 percent said they had used AI in assessments. Students also keep asking for clear rules. Jisc’s 2025 conversations with learners show that many remain unsure about what is allowed, even when guidance exists.
This post offers a practical way to manage AI in assessment integrity using policies, design choices, and supports you can implement inside PathBuilder. If you are new to our platform, see our short primers on AI in education and adaptive learning for context.
What “AI in assessment integrity” means in 2025
International guidance points to the same essentials. Set clear rules, build staff capacity, and protect learners as systems evolve. See UNESCO’s guidance for generative AI in education which was last updated on April 14, 2025.
In practice, aim for four outcomes.
- Clear, course-aware rules for acceptable AI use
- Assessment designs that capture authentic evidence of learning
- Proportionate review processes that respect due process
- Ongoing support for staff and students
A five-part framework you can apply now
1) Policy and governance anchored in your academic honesty policy
Update your academic honesty policy with concise generative AI guidelines that everyone can follow.
- Define allowed, limited, and prohibited uses for common tasks, such as brainstorming, grammar support, code scaffolding, or dataset creation. Tie examples to course outcomes.
- Require disclosure when AI is used. Ask for the tool name, where it was used, and how outputs were verified.
- Clarify evidence standards and appeals. Treat AI detection reports as one signal, not a verdict. Research summaries from Stanford HAI and a peer-reviewed study in Patterns show consistent false positives, especially for non-native English writers (Liang et al., 2023).
- Be transparent about detector settings. For example, Turnitin now withholds a numeric score for results below 20 percent and shows an asterisk to reduce false positives. See the latest note in their AI writing detection model update.
How PathBuilder helps
Add a policy page to each course template and attach a short disclosure prompt to key assignments. PathBuilder can keep acknowledgment records and display similarity results alongside student disclosures and draft history.
2) Assessment and rubric design that favors authentic work
Design tasks that produce verifiable evidence, then score that evidence with rubrics that reward process, attribution, and original reasoning.
Five design moves
- Require source-anchored responses. Students cite assigned materials, attach notes, or upload field artifacts.
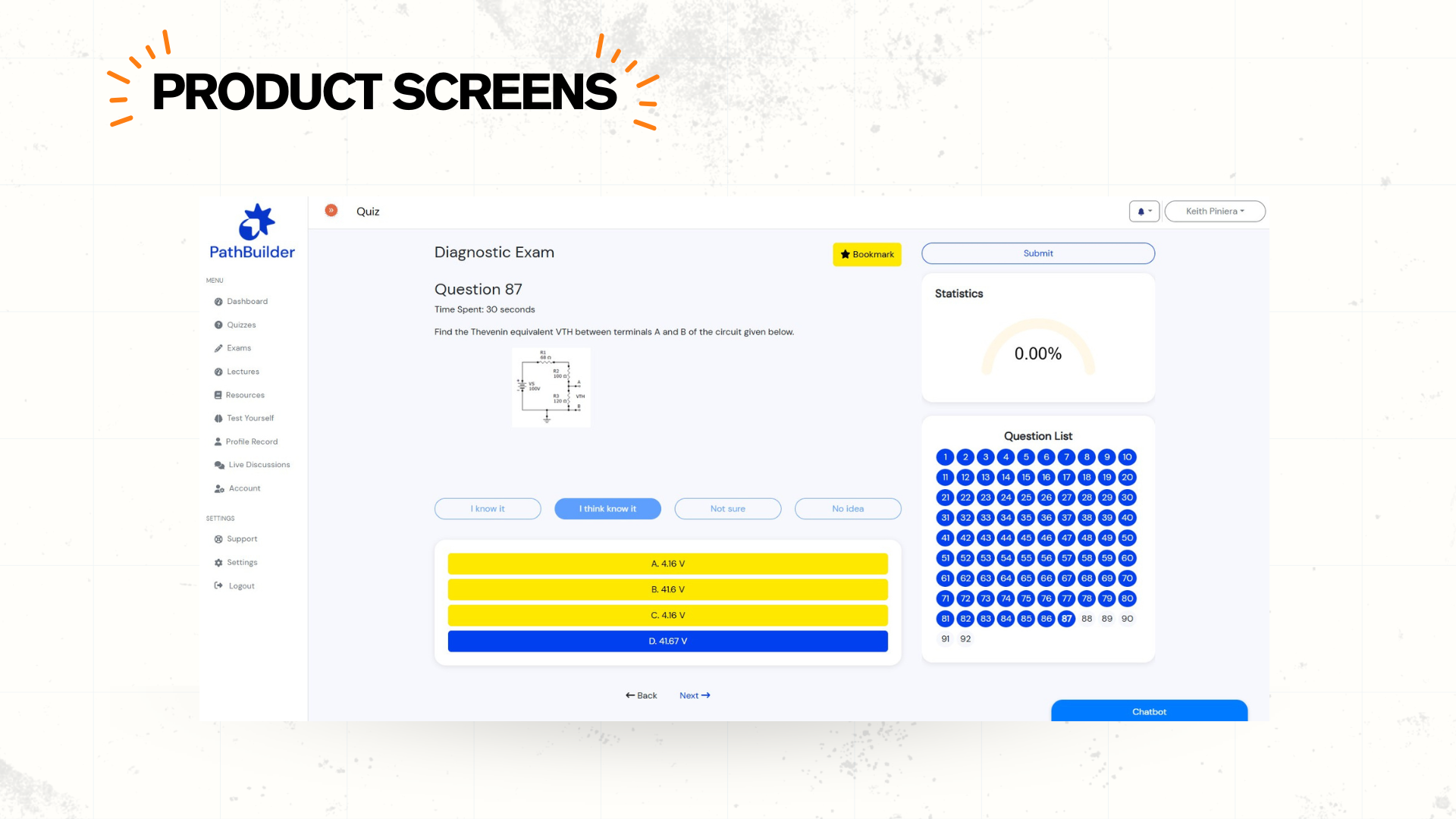
- Use staged submissions. Outline, draft, and final, with feedback checkpoints. Version history and timestamps form an evidence trail in PathBuilder.
- Add brief oral components. Short viva checks, explain-your-work videos, or lab debriefs confirm authorship.
- Rotate contexts. Same outcome, new data or scenario each term. Maintain a vetted bank of variants.
- For coding or data tasks, collect repos, commit logs, and testing output.
Rubric design tips
- Separate criteria for understanding, application, method, and attribution.
- Include a disclosure criterion that rewards accurate AI documentation and verification.
- Weight process and judgment, not only final polish.
- Provide examples of acceptable and unacceptable AI support inside the rubric notes.
3) Plagiarism prevention that fits AI
Similarity checks still help, but the design of the task is your first defense.
- Prompt for connections to course-specific sources or recent events
- Require annotated bibliographies or design logs
- Use unique datasets, case files, or local field observations
- Compare student drafts over time in PathBuilder
Keep AI detectors in perspective. The research above shows false positives are real and uneven across student groups. Use detectors as advisory signals and route concerns through a documented human review process.
4) Delivery controls and proctoring alternatives
Not every assessment needs high-stakes proctoring. A 2025 systematic narrative review in Open Praxis summarizes ongoing concerns about privacy, transparency, and fairness in online proctoring (Heinrich, 2025; ERIC mirror PDF). A 2024 study in the same journal reports mixed effects on course grades (Oeding, 2024; ERIC mirror PDF).
Proctoring alternatives you can deploy at scale
- Open-book and take-home exams that target higher-order skills with clear limits and time windows. See Ohio State’s short guide on alternatives to proctoring.
- Time-boxed problem sets with shuffled item banks and isomorphic variants
- Project and portfolio checks with short viva or demo recordings
- In-person practicals for competencies that require hands-on performance
- Code reviews and data audits where students explain approach and testing
Reserve live remote proctoring for assessments tied to external licensing or high-risk competencies and include accommodations from the start.
5) Support and culture
Make it simple to do the right thing.
- Staff training on designing AI-resilient tasks, reading disclosure statements, and interpreting similarity and detector signals
- Student orientation on acceptable AI use, disclosure, and citation in your context
- A resource hub with examples, a disclosure template, and discipline-specific advice
- Consistent course announcements and assignment checklists inside PathBuilder
Learners continue to ask for clarity and consistency, not just tools. See the trend summaries in Jisc’s 2025 report.
A sample policy insert you can adapt today
Use the wording below inside your academic honesty policy and course templates. It sets clear expectations, explains how to disclose AI use, and outlines a fair review path. Edit the examples to match your programs and accreditation rules.
Acceptable AI use
Students may use AI for idea generation, outlining, grammar support, and code linting when the assignment allows it. Students remain responsible for the accuracy, originality, and citation of all submitted work. If the level of permitted support is unclear, ask the instructor before using any tool.
With permitted uses defined, the next step is to make disclosure simple and consistent.
Disclosure
Any AI use must be documented in the submission. Include the tool name, where it was used, and a short note on how outputs were checked or adapted. Use the course’s standard disclosure field in PathBuilder so staff can view this alongside draft history.
If these conditions are not met, or if a task requires original creation, certain uses are not allowed.
Unacceptable AI use
Submitting AI generated text, code, or media as original work when the task requires personal analysis or creation is not allowed. The same applies to fabricated sources or data, or ignoring task-specific directions about AI use.
When questions arise, a clear and fair review process applies.
Review and appeals
When concerns are raised, staff will consider multiple signals, including similarity reports, writing patterns across drafts, short oral explanations, and any AI detector output. Detector scores are advisory only and are not used on their own for penalties. Students may appeal and share evidence such as notes, drafts, version history, and citations. Link this section to your full policy so students know where to find timelines and contacts.
Course design checklist for 2026
Use this list during course setup and pre-assessment reviews. Tick each item before the first high-stakes submission window.
Outcomes and planning
- Outcome map completed for every high-stakes task, with the expected level of AI support stated for each outcome
- Assessment blueprint shows weights, timing, and delivery mode for all tasks
- Program and course pages link to your academic honesty policy and generative AI guidelines
Task and rubric design
- Each assignment brief includes AI rules in plain language, with short allowed and not allowed examples
- Rubric includes criteria for disclosure, attribution, method, and original reasoning
- Staged submissions enabled for essays, reports, and code tasks, with at least one draft checkpoint
- At least one authorship check added per high-stakes task, for example a short viva or demo video
- Variant bank prepared for recurring tasks, with a simple rotation schedule and owner named
Delivery and integrity
- Similarity checks configured, with clear thresholds for manual review
- Any AI detector output treated as advisory only, routed through human review
- Integrity workflow set in PathBuilder, with roles, timelines, and documentation steps
- Proctoring plan defined by risk level, with proctoring alternatives in place where appropriate
- Accessibility and accommodations planned for all delivery modes
Student and staff support
- Student orientation module linked inside the course, including a short quiz on AI rules and disclosure
- Quick-reference guide for staff on reading disclosures and rubrics
- Template for AI disclosure available in the assignment submission area
- Communication plan scheduled, for example pre-task reminders and post-feedback notes
Monitoring and review
- Metrics set for disclosure rate, staged submission uptake, and time to resolve integrity cases
- Termly review meeting on assessment integrity scheduled, with actions recorded in PathBuilder notes
- Update cycle defined for variant banks, rubrics, and policy links
Metrics to track
- Disclosure rate per course or program
- Percentage of assessments using staged submissions
- Share of tasks that include an oral or demo component
- Similarity outliers investigated and resolved within a set time
- Student and staff confidence in policy clarity from pulse surveys
Where PathBuilder fits
PathBuilder supports this framework with course templates that include policy inserts and disclosure prompts, rubric libraries that reward process and attribution, version history to show draft progress, item banks for variants, and review workflows that combine similarity checks, disclosures, and notes in one place.
If you would like help aligning this with your institution’s policy, start with a quick scope session through our About page at Makarius Smart Learning or reach out to our team to experience the PathBuilder difference.















The PathBuilder team is a dynamic group of dedicated professionals passionate about transforming education through adaptive learning technology. With expertise spanning curriculum design, AI-driven personalization, and platform development, the team works tirelessly to create unique learning pathways tailored to every student’s needs. Their commitment to educational innovation and student success drives PathBuilder’s mission to redefine how people learn and grow in a rapidly changing world.